Data privacy isn’t just a tech buzzword anymore. It’s a global priority. In a world where data is the new oil, protecting personal information has become crucial. Enter the Digital Personal Data Protection (DPDP) Rules, 2025 — India’s latest move to establish a framework for safeguarding personal data.
If you’re wondering how this impacts you, your business, or even your online shopping habits, this article breaks it all down in simple terms. We’ll explore the DPDP Rules, their background, implications for industries, and actionable steps businesses need to take to stay ahead.
What Are the DPDP Rules, 2025?
The DPDP Rules, 2025, are part of India’s Digital Personal Data Protection Act, 2023. These rules set the groundwork for managing and processing personal data, aiming to balance individual privacy rights with the needs of businesses and government. Think of it as India’s own version of Europe’s GDPR, with some unique features tailored to India’s digital ecosystem.
Here’s a snapshot:
Purpose: To regulate the collection, storage, and use of personal data.
Scope: Covers private entities, government organizations, and even startups handling personal data in India.
Key Features: Transparency, consent-based processing, data security, and accountability for data breaches.
The Background: Why These Rules?
With India’s growing digital economy, personal data has become the lifeblood of industries ranging from e-commerce to healthcare. However, data misuse, breaches, and privacy violations have also increased. High-profile cases like the Aadhaar data breach and rising cyberattacks underscored the need for robust data protection laws.
Moreover, as global players like the EU (via GDPR) and the US set high privacy standards, India needed a comparable framework to:
Protect citizens’ data.
Attract global businesses.
Align with international trade agreements.
How Will the DPDP Rules Impact Different Industries?
How Will the DPDP Rules Impact Different Industries?
1. E-Commerce: The Balance Between Convenience and Privacy
India’s thriving e-commerce sector thrives on data — from personalized recommendations to seamless checkouts. Under the DPDP Rules, platforms like Flipkart and Amazon will need to rethink their strategies to ensure:
Explicit and Transparent Consent: Customers must clearly understand how their data will be used, whether for targeted ads or product suggestions.
Data Minimization: Collect only what’s necessary. For instance, storing payment data indefinitely will no longer be permissible unless justified.
Challenges: Retaining a personalized shopping experience while respecting privacy can be a tricky balance. Additionally, smaller e-commerce platforms may struggle with the technical expertise to comply.
2. Banking and Insurance (BFSI): Securing Trust in Sensitive Transactions
With financial institutions managing critical data like Aadhaar and transaction details, the BFSI sector must:
Enhance Security Protocols: Breaches can now lead to direct notifications to affected customers, potentially eroding trust.
Introduce Consent-Driven Cross-Selling: Insurers must ensure that upselling policies or loans comes with informed customer approval.
Sector-Specific Concern: Balancing compliance costs with ROI, especially for regional banks and smaller insurers.
3. Technology and Social Media: The Localization Debate
Tech giants like Meta and Google, with massive user bases, face unique challenges:
- Localization Requirements: Ensuring data stays within India’s borders could mean significant investment in local infrastructure.
- Accountability for Algorithms: Platforms will need to audit their algorithms for bias or unintended consequences.
- Impact: This could influence the way users experience ads and content. Expect fewer tailored ads initially as companies adapt.
4. Healthcare: Balancing Innovation with Privacy
India’s booming health-tech sector often deals with deeply personal data. Hospitals, apps, and clinics will need to:
- Redefine Consent: Patients must be explicitly informed how their health data will be used. Apps collecting fitness data, for example, cannot pass this to third-party advertisers without clear permission.
- Challenges: Many health-tech startups might find integrating these protocols daunting given the sensitivity of medical data and the resources required.
5. Online Gaming: More Than Just Fun
With millions logging in daily, online gaming platforms must ensure Age Verification: Prevent minors from accessing age-inappropriate games. Retention Limits: Only keep data as long as it’s relevant to enhance user safety and engagement.
Sector Struggles: Smaller gaming startups may face compliance burdens as the cost of ensuring data privacy rises.
6. Startups and SMEs: The Cost of Compliance
While these rules aim to protect consumers, startups may struggle due to Budget Constraints: Unlike larger firms, most startups don’t have dedicated legal or tech teams to handle compliance.
Opportunities for Innovation: On the flip side, compliance-focused startups (like consent management tools) have a chance to thrive.
Steps Businesses Should Take to Comply with DPDP Rules
Steps Businesses Should Take to Comply with DPDP Rules
Complying with the DPDP Rules is not just a legal requirement but a critical step toward safeguarding customer trust and ensuring operational longevity. Here’s a deeper dive into actionable steps businesses should take:
Complying with the DPDP Rules is not just a legal requirement but a critical step toward safeguarding customer trust and ensuring operational longevity. Here’s a deeper dive into actionable steps businesses should take:
Appoint a Data Protection Officer (DPO):
Appoint a Data Protection Officer (DPO):
A dedicated DPO ensures accountability. This individual oversees compliance, manages breach responses, and interacts with the Data Protection Board if needed. For smaller firms, outsourcing this role to a privacy consultancy might be a viable option.
Conduct a Data Audit
Conduct a Data Audit
Understand what data you collect, how it’s stored, and who has access. Categorize data by sensitivity and identify areas of risk. Example: If you’re an e-commerce business, ensure customer payment data is encrypted and stored securely.
Invest in Consent Management Systems:
Build or adopt platforms that make it easy for users to give, withdraw, and manage their consent. Example: An app that collects location data must provide a clear toggle for users to opt in or out.
Build or adopt platforms that make it easy for users to give, withdraw, and manage their consent. Example: An app that collects location data must provide a clear toggle for users to opt in or out.
Implement Robust Security Measures:
Implement Robust Security Measures:
Encrypt all sensitive data both at rest and in transit.
Set up firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and regular vulnerability assessments.
Example: A healthcare provider must ensure patient records are inaccessible to unauthorized personnel.
Establish Incident Response Plans:
Establish Incident Response Plans:
Prepare a step-by-step protocol for handling data breaches. This includes notifying affected users and the Data Protection Board within stipulated timelines.
Focus on Employee Training:
Focus on Employee Training:
Train employees to recognize phishing attacks, handle sensitive data responsibly, and understand compliance requirements.
Example: Equip customer support teams to address data-related queries accurately.
Collaborate with Legal and Privacy Experts:
Collaborate with Legal and Privacy Experts:
Regularly consult with legal experts to ensure your policies and practices align with the evolving regulatory landscape.
Build Data Localization Strategies:
If your business involves cross-border data transfers, establish localized data storage solutions to comply with the rules. Collaborate with cloud providers offering in-country data centers.
Establish Transparent Data Retention Policies:
Define how long different types of data are retained and ensure automated deletion once the purpose is fulfilled.
Example: An online gaming company might delete player data three years after inactivity unless required otherwise.
Conduct Regular Compliance Reviews:
By taking these steps, businesses can not only avoid penalties but also foster a culture of trust and transparency that customers increasingly value in today’s digital age.
Penalties and Implications of Non-Compliance
Penalties and Implications of Non-Compliance
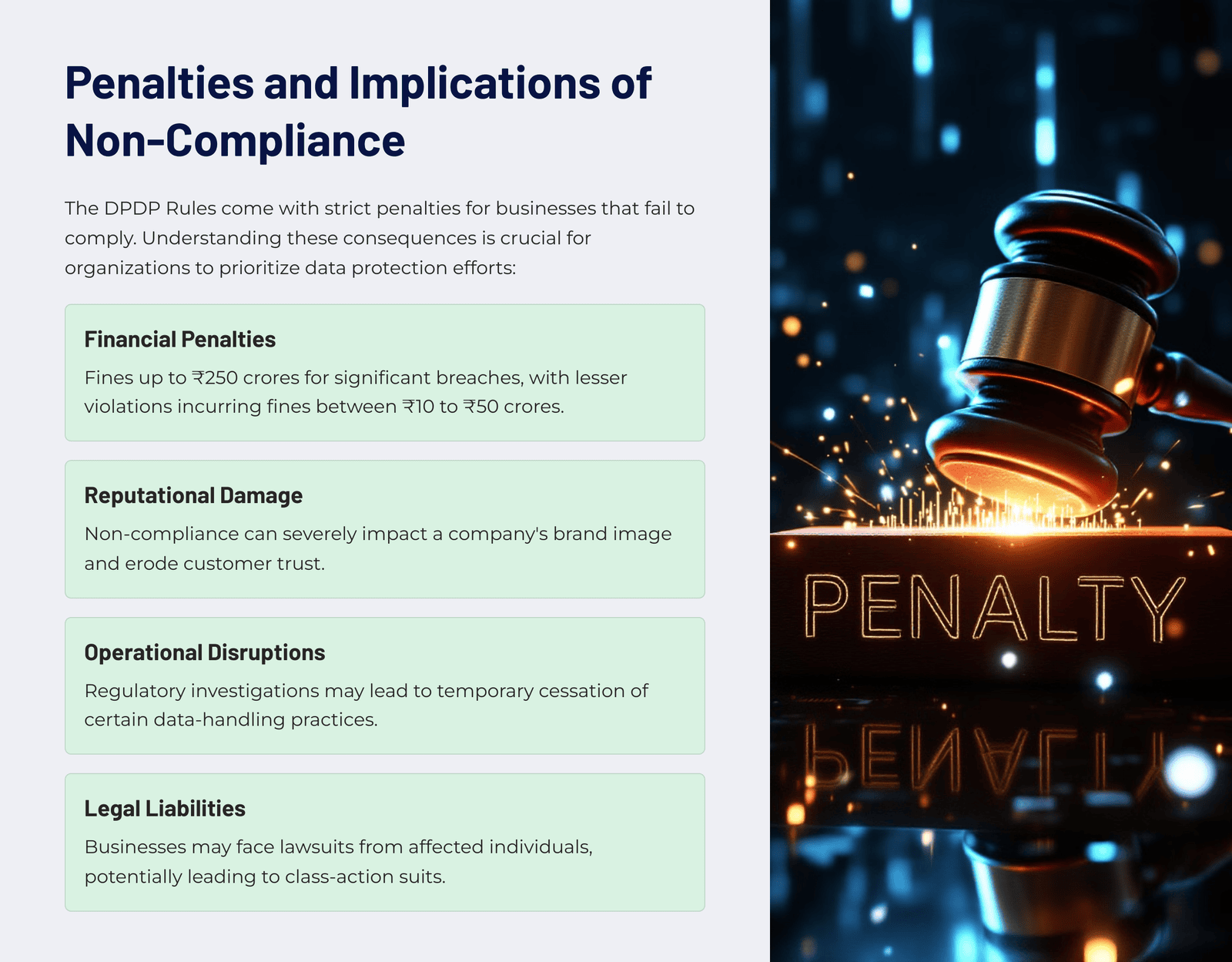
Case Study Example: In a recent global incident, a major tech company was fined $1.2 billion under GDPR for transferring user data to servers in a non-compliant manner. The case highlighted not just the financial penalty but also operational restrictions imposed on the company, forcing it to alter its data processing practices globally. With DPDP in place, similar scenarios could unfold in India. For instance, a domestic social media platform failing to notify users of a breach could face hefty fines up to ₹250 crores. Beyond fines, such violations may lead to operational disruptions, such as suspension of data transfers or usage bans, creating a ripple effect on business reputation and user trust.
Opportunities for Businesses
Enhanced Customer Trust: Compliance shows customers you value their privacy, strengthening brand loyalty.
Competitive Advantage: Early adopters of robust data protection can differentiate themselves in the market.
Global Readiness: Aligning with DPDP also prepares businesses for international data protection standards like GDPR.
What’s Next for India?
India’s DPDP Rules are a major step towards creating a safe digital ecosystem. But challenges remain:
Awareness: Many businesses, especially SMEs, lack knowledge about compliance requirements.
Costs: Implementing secure systems and audits can strain smaller enterprises.
Enforcement: The success of these rules depends on rigorous enforcement by authorities.
Despite these hurdles, the DPDP Rules are a long-awaited move towards protecting personal data in India’s rapidly digitizing economy.

Download Our Comprehensive Guide to DPDP Compliance
Want to dive deeper into the nuances of the Digital Personal Data Protection (DPDP) Rules, 2025? Our Comprehensive Guide to DPDP Compliance is here to help! This detailed document covers everything you need to know, including actionable steps for businesses, case studies, penalties for non-compliance, and best practices to ensure you’re fully prepared.
Whether you're a startup, an established enterprise, or a government organization, this guide is tailored to equip you with the insights and tools to navigate these regulations seamlessly. Click here to download your copy now and take the first step toward data protection excellence!
Conclusion
The Digital Personal Data Protection Rules, 2025, are not just another regulation. They represent a paradigm shift in how India views data privacy. Whether you’re a consumer enjoying online shopping or a business navigating the digital space, these rules will shape the future of India’s digital landscape.
By prioritizing transparency, consent, and security, the DPDP Rules aim to create a win-win for individuals and businesses. As India steps into this new era of data protection, being proactive is the best strategy. After all, data is not just about numbers — it’s about trust.
What do you think about the new rules? Are you ready for this data revolution? Let us know in the comments!
Disclaimer
This article is for informational purposes only and does not constitute legal or insurance advice. Businesses should consult qualified professionals to evaluate their specific needs and risks before taking action.



